Three-dimensional (3D) rendering has revolutionized industries by bringing concepts and designs to life in ways that were previously unimaginable. 3D renders are digitally created images that mimic real-world objects, environments, and textures with extraordinary accuracy. They are not merely visual aids; they are tools for communication, innovation, and creativity. Across architecture, entertainment, product design, and marketing, 3D rendering offers a powerful means to visualize ideas, streamline workflows, and captivate audiences.
The process of creating 3D renders begins with modeling, where the structure or form of an object is digitally sculpted. Using specialized software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max, designers meticulously construct shapes and contours that replicate the intended design. Texturing follows, applying surface details such as colors, patterns, and materials to give the object realism. Lighting and shading bring depth and atmosphere, creating shadows and highlights that enhance the object’s dimensionality. Finally, rendering transforms these elements into high-resolution images or animations.
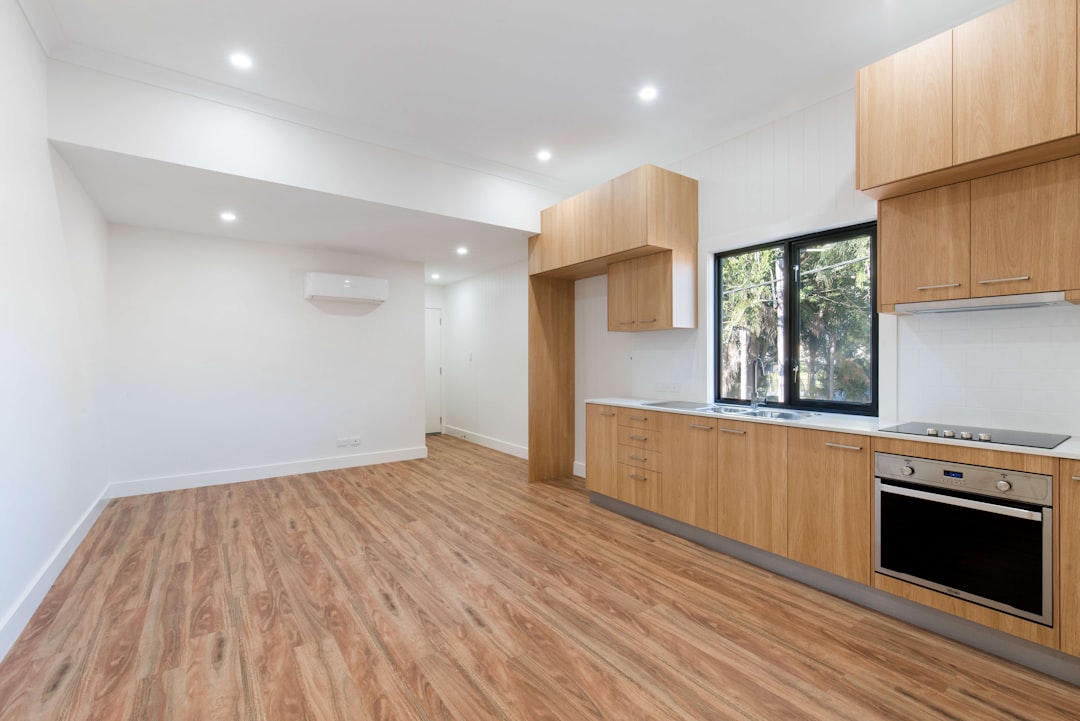
In architecture and real estate, 3D renders play a pivotal role in showcasing designs before construction begins. Clients and stakeholders can visualize buildings, interiors, and landscapes with stunning clarity, enabling them to make informed decisions. Virtual walkthroughs and photorealistic images allow for an immersive experience that traditional blueprints or 2D drawings cannot provide. Designers can experiment with different layouts, materials, and lighting conditions, optimizing the final design and avoiding costly revisions during construction.
For product design, 3D rendering is a game-changer. It enables designers to prototype concepts digitally, reducing the need for physical models. This not only saves time and resources but also allows for greater flexibility in exploring variations. Companies can use 3D renders for marketing even before the product is manufactured, creating compelling visuals for advertisements, e-commerce platforms, and promotional materials. High-quality renders make products stand out, emphasizing their features and functionality in ways that photographs sometimes cannot.
The entertainment industry relies heavily on 3D rendering to create immersive worlds and stunning visual effects. From animated films and video games to virtual reality (VR) experiences, 3D renders are the foundation of storytelling. They bring characters to life, craft realistic environments, and simulate dynamic elements such as water, fire, and weather. Advances in rendering technology, such as ray tracing, have elevated the quality of visuals, achieving levels of realism that blur the line between virtual and real.
Marketing and branding also benefit significantly from 3D rendering. Brands use renders to create impactful visuals that capture attention and convey their message effectively. From sleek product showcases to vibrant event promotions, 3D renders provide the creative freedom to explore innovative ideas. With the rise of augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR), 3D renders have become instrumental in creating interactive and engaging customer experiences. Virtual try-ons and immersive product demonstrations are just a few examples of how brands leverage 3D technology to connect with their audience.
The flexibility of 3D rendering extends to customization and personalization. Designers can adapt renders to suit specific audiences, modifying details like colors, textures, or configurations without the need for additional resources. This adaptability is particularly valuable in industries like automotive or interior design, where clients often seek bespoke solutions. Configurators powered by 3D rendering allow users to visualize different options in real-time, enhancing their decision-making process and satisfaction.
Lighting is a critical component in 3D rendering, influencing the mood, realism, and aesthetic appeal of the final output. Whether it’s natural sunlight streaming through windows or the soft glow of artificial lights, precise lighting setups transform scenes into lifelike representations. Designers experiment with intensity, direction, and color to achieve the desired ambiance, often drawing inspiration from photography and cinematography. Advanced techniques like global illumination and ambient occlusion simulate the behavior of light in real-world scenarios, adding depth and authenticity to the render.
Textures and materials are equally important in achieving realism. From the roughness of concrete to the sheen of polished metal, detailed textures give objects their character and believability. Physically Based Rendering (PBR) techniques have become the industry standard, accurately replicating how materials interact with light. By incorporating high-quality texture maps for elements like diffuse color, specularity, and normal depth, designers can create renders that are indistinguishable from reality.
Another remarkable aspect of 3D rendering is its application in simulations and virtual testing. Engineers and scientists use renders to model complex systems, study behaviors, and test scenarios in a virtual environment. In industries like aerospace or healthcare, these simulations provide valuable insights, enabling innovation while reducing risks and costs. For example, medical professionals can visualize anatomical structures in 3D, improving diagnosis and surgical planning. Similarly, engineers can simulate aerodynamic properties of vehicles, optimizing designs for efficiency and performance.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the possibilities of 3D rendering. Real-time rendering engines, such as Unreal Engine and Unity, have brought interactive visualization to the forefront. These tools enable designers to explore scenes dynamically, making adjustments on the fly and receiving immediate feedback. This capability is particularly valuable in VR and AR applications, where user interaction is key. The advent of AI-driven tools has further streamlined the rendering process, automating tasks like texture creation, lighting optimization, and asset generation. By reducing manual effort, these innovations empower designers to focus on creativity.
Collaboration is central to the success of 3D rendering projects. Teams of designers, animators, and technical specialists work together, pooling their expertise to achieve a shared vision. Cloud-based platforms have facilitated this collaboration, allowing stakeholders from different locations to contribute and review progress in real time. This interconnected approach ensures that the final renders align with client expectations and project objectives.
Data management is an essential consideration in 3D rendering, as the process generates large volumes of files and assets. Efficient workflows and robust storage solutions are critical for maintaining productivity and safeguarding work. Designers rely on structured file naming conventions, version control systems, and scalable hardware to handle the demands of rendering. With the increasing adoption of cloud services, teams can access resources and render farms remotely, accelerating production timelines.
Environmental sustainability is becoming a priority in the rendering industry. The computational power required for high-quality renders consumes significant energy, prompting the need for greener practices. Energy-efficient hardware, optimized software algorithms, and renewable energy sources for data centers are some of the measures being adopted. Additionally, virtual prototyping and digital simulations reduce the environmental impact associated with physical models and prototypes, contributing to a more sustainable workflow.
The future of 3D rendering is poised for exciting advancements. Photorealism will continue to improve with innovations in rendering algorithms, hardware capabilities, and AI integration. The convergence of 3D rendering with other technologies, such as 3D printing and robotics, will open new possibilities for design and manufacturing. As these technologies evolve, 3D rendering will remain at the forefront of visual communication, pushing creative boundaries and transforming industries.